Blog Number:-001
Hello Everybody,
Well, I wish you all will be good and healthy.
Today we are going to start our Topics. So before starting the topic, lets have a quick look what we are going to discuss today.
We will discuss- resistor.
Resistor:-
Introduction:
Thats all for the session, If you have any query related to the topic, then feel free to ask.
Hello Everybody,
Well, I wish you all will be good and healthy.
Today we are going to start our Topics. So before starting the topic, lets have a quick look what we are going to discuss today.
We will discuss- resistor.
Resistor:-
Introduction:
 |
| Resistor |
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses.
High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators.
There are two types of Resistor:-
1. Fixed resistor(Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage.)
2. Variable resistor(Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer, or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity.)
Representation Of Resistor:
Theory Of Operation:
Ohm's Law-
The behavior of an ideal resistor is dictated by the relationship specified by Ohm's law:
Ohm's law states that the voltage (V) across a resistor is proportional to the current (I), where the constant of proportionality is the resistance (R).
Practical resistors also have some inductance and capacitance which affect the relation between voltage and current in alternating current circuits.
The ohm (symbol: Ω) is the SI unit of electrical resistance. An ohm is equivalent to a volt per ampere.
The total resistance of resistors connected in series is the sum of their individual resistance values.
The total resistance of resistors connected in parallel is the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistors.

- Power dissipation-
- At any instant, the power P (watts) consumed by a resistor of resistance R (ohms) is calculated as: where V (volts) is the voltage across the resistor and I (amps) is the current flowing through it.
 |
| a. Fixed Resistor; b. Rheostat; c. Potentiometer |
Thats all for the session, If you have any query related to the topic, then feel free to ask.
Thank You,
Er. Rahul Kumar


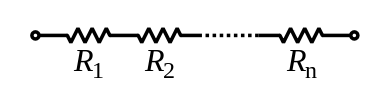



how do resistors divide voltage?
ReplyDeleteWhen the resistor are connected in series followed by a voltage source available to the network
Delete