Blog number:-022
Hello everybody.
I hope you all will be fine.
In the last session we discussed about DC Motor. So, in this session we will discuss about a special type of DC Motor called Servo Motor
Servo Motor:-



Hello everybody.
I hope you all will be fine.
In the last session we discussed about DC Motor. So, in this session we will discuss about a special type of DC Motor called Servo Motor
Servo Motor:-
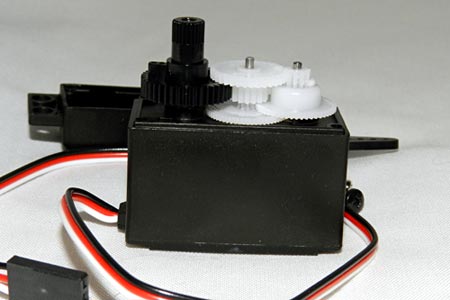
Servo motors (or servos) are self-contained electric devices that rotate or push parts of a machine with great precision. Servos are found in many places: from toys to home electronics to cars and airplanes. And of course robots might not exist without servos.
Or, A servomotor is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and acceleration.It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also requires a relatively sophisticated controller, often a dedicated module designed specifically for use with servomotors.
How does a servo motor work?
Mechanism-A servomotor is a closed-loop servomechanism that uses position feedback to control its motion and final position. The input to its control is a signal (either analogue or digital) representing the position commanded for the output shaft.
The simplicity of a servo is among the features that make them so reliable. The heart of a servo is a small direct current (DC) motor. These motors run on electricity from a battery and spin at high RPM (rotations per minute) but put out very low torque (a twisting force used to do work— you apply torque when you open a jar). An arrangement of gears takes the high speed of the motor and slows it down while at the same time increasing the torque. (Basic law of physics: work = force x distance.) A tiny electric motor does not have much torque, but it can spin really fast (small force, big distance). The gear design inside the servo case converts the output to a much slower rotation speed but with more torque (big force, little distance). The amount of actual work is the same, just more useful. Gears in an inexpensive servo motor are generally made of plastic to keep it lighter and less costly. On a servo designed to provide more torque for heavier work, the gears are made of metal and are harder to damage.


With a small DC motor, you apply power from a battery, and the motor spins. Unlike a simple DC motor, however, a servo's spinning motor shaft is slowed way down with gears. A positional sensor on the final gear is connected to a small circuit board. The sensor tells this circuit board how far the servo output shaft has rotated. The electronic input signal from the computer or the radio in a remote-controlled vehicle also feeds into that circuit board. The electronics on the circuit board decode the signals to determine how far the user wants the servo to rotate. It then compares the desired position to the actual position and decides which direction to rotate the shaft so it gets to the desired position.

Imagine you are playing catch with a friend on a sports field. You stand at one end and want your friend to go out for a long throw. You could keep calling out "farther, farther, farther" until she got as far away as you wanted. But if she went out farther than you can throw, you would have to call out "closer" until she got back to the right spot. If she were a simple motor in a robot arm and you were the microprocessor, you would have to spend some of your time watching what she did and giving her commands to move her back to the right spot (this is called a feedback loop). If she were a servo motor, you could just say "go out exactly 4.5 meters" and know that she would find the right spot. That is what makes servo motors so useful: once you tell them what you want done, they do the job without your help. This automatic seeking behavior of servo motors makes them perfect for many robotic applications.
DC Servo Motor Block Diagram
A servo motor consists of a DC motor, reduction gearbox, positional feedback device and some form of error correction(feedback loop). The speed or position is controlled in relation to a positional input signal or reference signal applied to the device.
The error detection amplifier looks at this input signal and compares it with the feedback signal from the motors output shaft and determines if the motor output shaft is in an error condition and, if so, the controller makes appropriate corrections either speeding up the motor or slowing it down.
A servo motor consist of several devices in one package, the motor, gearbox, feedback device and error correction for controlling position, direction or speed. They are widely used in robotics and small models as they are easily controlled using just three wires, Power, Ground and Signal Control.
So, that's all for this session. If you have any doubt related to topic, Please comment
Thank you.

No comments:
Post a Comment